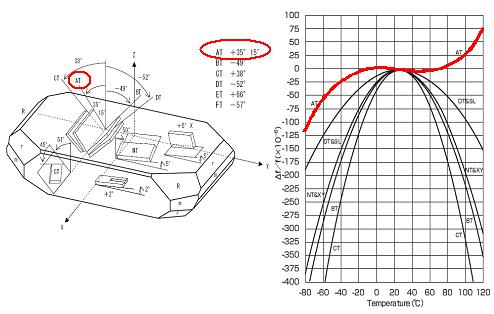
(AT切割角度+35°15’时,石英晶体的频率温度特性比其它切角表现更稳定)
Since the piezoelectric effect was discovered in quartz crystals in 1880, we have known that an electric potential will appear across certain faces of a crystal when it is subjected to mechanical pressure.
自从在石英晶体中发现了压电效应的物理特性,我们就了解到当它受到机械压力时,晶体的某些面上会出现电势。
According to different cut angles to quartz bars, there are different kinds of quartz plates, for examples, AT, BT, CT-cut plates different types of quartz cuts, have different available elastic, piezoelectric and different properties, which are the basic parameters for designing a quartz crystal device. The most often used Quartz- cut types are AT-cut angle +35° 15’ shown as below figures schematically.Especially, the frequency-temperature characteristic of AT-cut angle is more stable than other cut angles, which is also the cutting way most commonly used in Genuway Factory.
根据石英棒切割角度的不同,石英晶片有不同的种类,例如AT、BT、CT切割板等不同类型的石英切割,具有不同的可用弹性、压电和不同的性能,这些都是设计石英晶体器件的基本参数。最常用的石英切割类型是AT切割角度+35°15’。特别是AT切角的频率温度特性比其它切角更稳定,因此这也是晶诺威科技目前最常用的晶片切割方式。
附:
1880年法国人P.居里和J.居里兄弟发现石英晶体受到压力时,它的某些表面上会产生电荷,电荷量与压力成正比;称这种现象为压电效应;具有压电效应的物体称为压电体。
居里兄弟还证实了压电体具有逆压电效应,即在外电场作用下压电体会产生形变。压电晶体的对称性较低,当受外力作用产生形变时单胞中正负离子的相对位移使得正负电荷中心出现不相等的移动,导致晶体发生宏观极化;而晶体表面电荷密度等于极化强度在表面法向上的投影,故晶体受压力形变时表面出现电荷。