QUARTZ CRYSTALS
Synthetic quartz is composed of silicon and Oxygen (Silicon Dioxide) and is cultured in autoclaves under high pressure and temperature. Quartz exhibits piezoelectric properties. This device generates an electrical potential when pressure is applied on the surfaces of the crystal. Conversely, when an electrical potential is applied to the surface of a crystal mechanical deformation or vibrations are generated. These vibrations occur at a frequency determined by the crystal design and oscillator circuit.
- TYPE/ANGLE OF QUARTZ CUT
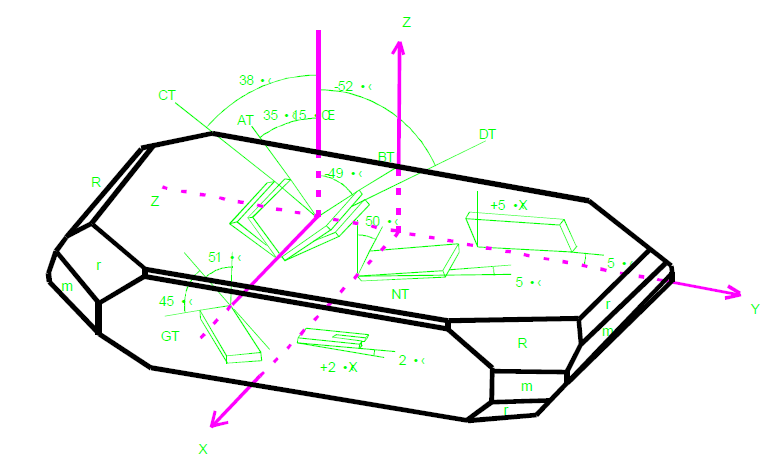
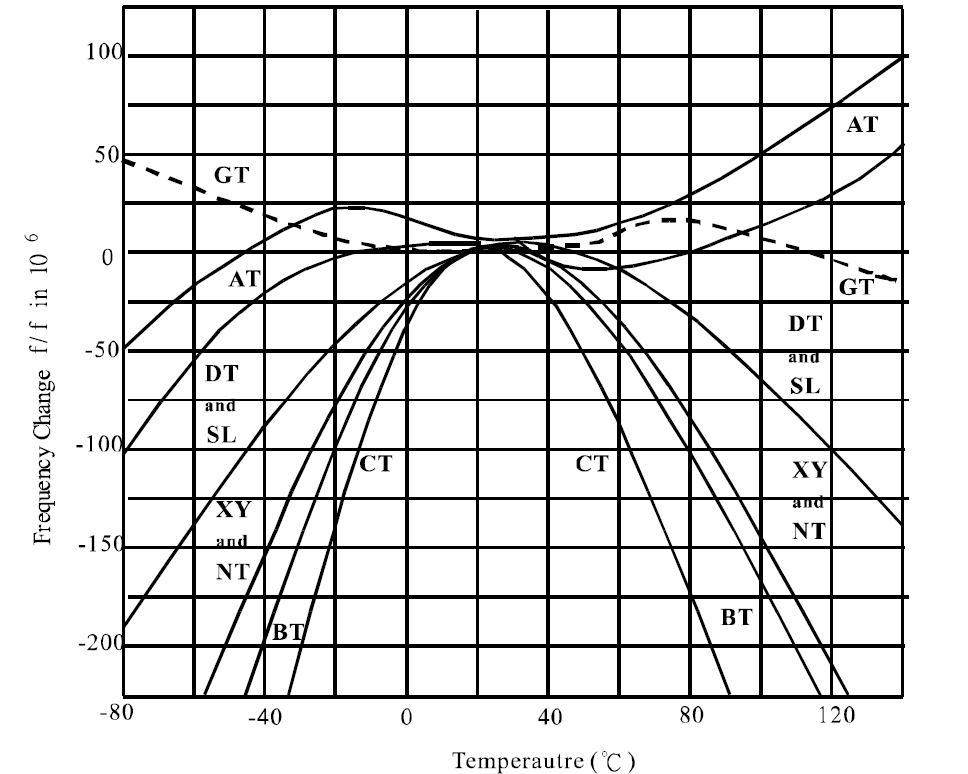
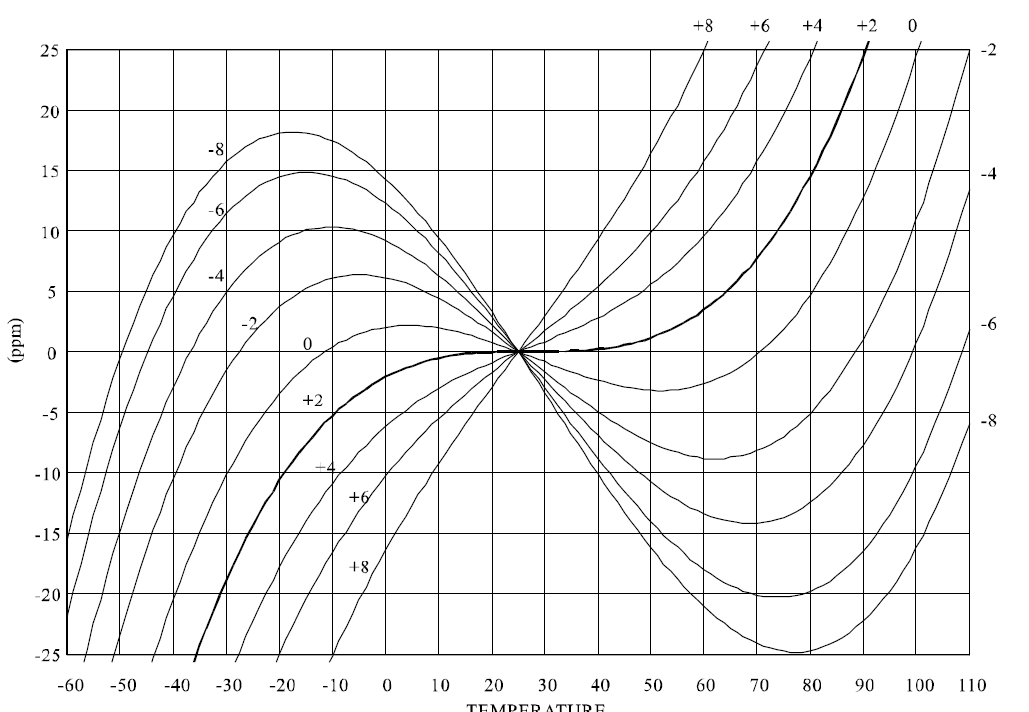
The type and angle of a quartz cut effects the crystal device operating parameters the most significant being frequency stability. The frequency stability is dependant on the plane or the angle of the crystal. The plane or angle is referred to as the crystal “cut”. As shown in Figure 1a common type of thickness shear crystal fabricated from Y bar quartz is the “AT” cut. In Figure 2the frequency stability versus operating temperature range is plotted as a function of “AT” cut angle. Note the inflection point at approximately 25℃ and the location of the adjacent upper and lower turning points for each cut angle. The frequency stability and operating temperature range required by the customer determine the angle of cut utilized.
(Orientation angle of Z-plate quartz crystal)
(AT-cut frequenncy -temperature characteristics)
- CENTER FREOUENCY
The specified center frequency of the crystal is typically specified in megahertz (MHz) or kilohertz (KHz)
- FREQUENCY TOLERANCE OR CALIBRATION ACCURACY
The amount of frequency deviation from a specified center frequency at ambient temperature(referenced at25℃).This parameter is specified with a maximum and minimum frequency deviation, usually expressed in parts permillion (ppm).This deviation is associated with a set of operating condition including Load capacitance and drive level.
- FREQUENCY STABILITY
Frequency Stability is the amount of frequency deviation from the ambient temperature frequency. This deviation is associated with a set of operating conditions including: Operating Temperature Range, Load Capacitance, and Drive Level. This parameter is specified with a maximum and minimum frequency deviation, usually expressed in parts per million(ppm). The frequency stability is determined by the following factors: type of quartz cut, angle of the quartz cut, mode of operation, and mechanical design of the quartz blank.
- DRIVE LEVEL (DL)
A function of the driving or excitation current is flowing through the crystal. The drive level is the amount of power dissipation in the crystal, usually expressed in microwatts.
Maximum power is the most power the device can dissipate while still maintained operation with all electrical parameters guaranteed. Drive level should be maintained at the minimum levels necessary to assure proper start-up and steady state oscillation, thus avoiding poor aging characteristics and crystal damage.
- SHUNT CAPACITANCE(C0)
The static capacitance between the crystal terminals.
Measured in picofarads (pF), Shunt Capacitance is present whether the device is oscillating or not (unrelated to the piezoelectric effect of the quartz).Shunt Capacitance is derived from the dielectric of the quartz, the area of the crystal electrodes, and the capacitance presented by the crystal holder.