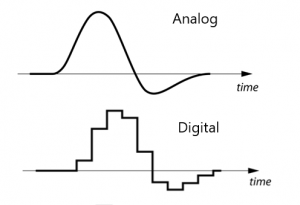
Basically, there are two types of signals, i.e., analog signals and digital signals.
从基本上来看,信号分为两种类型,即模拟信号和数字信号。
- Analog signals模拟信号
Analog signal is a continuous time-varying signal that has an infinite amount of samples in it. These analog signals are further divided into composite and simple analog signals. Sinusoidal waves being simple analog signals and all the others, composite signals, are made from the combination of multiple variants of simple sinusoidal waves.
模拟信号是一个连续的时变信号,它含有无限数量的采样。这些模拟信号又进一步分为复合模拟信号和简单模拟信号。正弦波是简单的模拟信号,其他的都是合成信号,是由简单正弦波的多种变体组合而成的。
- Digital signals数字信号
Digital signals also carry data just like analog signals, but in the case of digital signals, these values are discrete. It represents data in the form of a discrete sequence of values and is defined by interval or the bit rate. The digital signals thus contain a set of numbers that depict the samples of a continuous variable.
数字信号也像模拟信号一样携带数据,但在数字信号的情况下,这些值是离散的。它以离散值序列的形式表示数据,并由区间或比特率定义。因此,数字信号包含一组描述连续变量样本的数字。
The picture above represents the same signal in both analog and digital form. Note that the edges in the digital signal represent the point at which the sample was taken.
上图分别以模拟和数字形式表示相同的信号。请注意,数字信号中的边缘代表采样点。
注:
在数字电路中,无源晶振输出为正弦波信号,经由整形电路整形为方波后,供给下级电路。有源晶振一般输出为方波为主,可直接供给下级电路使用。
拓展阅读:复杂环境中模拟图传和数字图传的抗干扰能力怎么样?
在复杂环境中,模拟图传和数字图传的抗干扰能力有明显差异:
1. 模拟图传的抗干扰能力
抗干扰能力较弱:模拟图传容易受到环境中电磁干扰的影响,例如建筑物、树木、其他无线电设备等,都会对模拟图传的信号质量产生显著影响。
信号劣化逐渐:当受到干扰时,模拟图传信号会逐渐下降,表现为图像出现噪点、条纹或雪花。随着干扰增加,图像质量逐渐变差,但不会直接中断。
穿透能力有限:在穿透建筑或障碍物的环境下,模拟图传的信号衰减较大,因此在这种场景下较难保证稳定的图像质量。
2. 数字图传的抗干扰能力
抗干扰能力较强:数字图传采用编码技术,并通过错误纠正和数据重传机制,在一定程度上能够抵御电磁干扰,使图像质量在受干扰时保持清晰稳定。
图像劣化方式不同:在复杂环境中受到较强干扰时,数字图传一般不会出现模拟图传的噪点和条纹,而是直接表现为卡顿、延迟增加或画面冻结(也就是“断续”现象)。
频段灵活:数字图传可以使用多个频段(如2.4GHz和5.8GHz),并结合自适应频率跳变技术,能够选择干扰较小的频段进行传输,从而提高信号的稳定性和抗干扰能力。
穿透性增强:一些高性能的数字图传设备还具备较强的信号穿透能力,可以在一定程度上穿透障碍物,实现更广的覆盖范围。