What is Jitter in a Crystal Oscillator? 什么是晶体振荡器中的抖动?
Jitter is a method of describing the stability of an oscillator in the Time Domain. It combines all the noise sources together and shows their effect with respect to time.
抖动是一种描述振荡器在时域中稳定性的方法。它将所有噪声源组合在一起,并显示它们相对于时间的影响。
Let us consider a simple pulsed signal chain. Ideally, the duration of a perfectly pulsed signal at a frequency of 1 MHz, would be exactly every 1 microseconds, with an alternating edge every 500 ns (See the Figure below).
让我们考虑一个简单的脉冲信号链。理想情况下,频率为1 MHz的完美脉冲信号的持续时间正好是每1微秒一次,每500 ns交替边沿一次(见下图)。
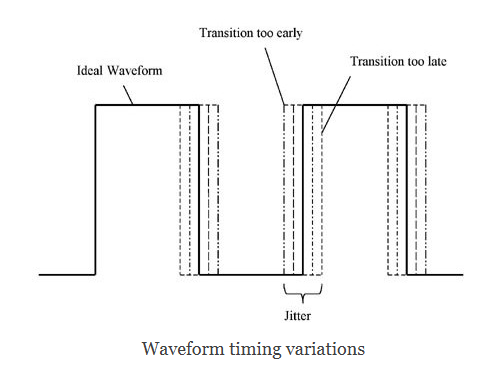
But in the real world, this does not happen. In reality, the position and amplitude of the alternating edge varies, which causes uncertainty about when the next edge of the signal will occur. This uncertainty is know as Jitter (time domain) and phase noise (frequency domain).
但在现实世界中,这不会发生。实际上,交替边沿的位置和幅度各不相同,这导致信号的下一个边沿何时出现不确定。这种不确定性称为抖动(时域)和相位噪声(频域)。
Jitter measures the variations of signal period in the time domain, describing how far the signal period has wandered from its ideal value. Typically, deviations below 10 MHz are not classified as jitter, but as wander or drift.
抖动测量信号周期在时域中的变化,描述信号周期偏离其理想值的距离。通常,低于10 MHz的偏差不被归类为抖动,而是被归类为漂移。
There are two main types of jitter: deterministic and random.
抖动主要有两种类型:确定性和随机性。
Deterministic Jitter is created by identifiable interference signals. It is always bounded in amplitude, has specific (not random) causes, and cannot be analyzed statistically.
确定性抖动由可识别的干扰信号产生。它总是有振幅限制,具有特定(非随机)原因,并且无法进行统计分析。
There are four main sources of deterministic jitter:
确定性抖动有四个主要来源:
![]() Crosstalk between adjacent signal traces 相邻信号走线之间的串扰
Crosstalk between adjacent signal traces 相邻信号走线之间的串扰
![]() EMI radiation on a sensitive signal path敏感信号路径上的 EMI 辐射
EMI radiation on a sensitive signal path敏感信号路径上的 EMI 辐射
![]() Noise from power layers of a multi-layer substrate多层基板功率层的噪声
Noise from power layers of a multi-layer substrate多层基板功率层的噪声
![]() Simultaneous switching of multiple gates to the same logic state同时将多个门切换到相同的逻辑状态
Simultaneous switching of multiple gates to the same logic state同时将多个门切换到相同的逻辑状态
Random Jitter describes timing variations caused by less predictable influences like temperature which can affect the mobility of semiconductor crystal material, or semiconductor process variations etc.
随机抖动描述了由不太可预测的影响引起的时序变化,例如温度会影响晶体半导体材料的迁移率或半导体工艺变化等。







