What is Ultra Wideband Technology (UWB)? 什么是超宽带技术(UWB)?
Before anything, let us learn what exactly is Ultra Wideband Technology in lucid terms. Just like WiFi and Bluetooth, Ultra Wideband Technology (shortly known as UWB) is a wireless technology. It leverages radio signals to communicate and transfer data between different devices. But there are some distinct characteristics of UWB that make it a powerful radio technology.
首先,让我们清楚地了解一下超宽带技术到底是什么。就像WiFi和蓝牙一样,超宽带技术(简称UWB)是一种无线技术。它利用无线电信号在不同设备之间进行通信和传输数据。但是UWB有一些明显的特征,使其成为一种强大的无线电技术。
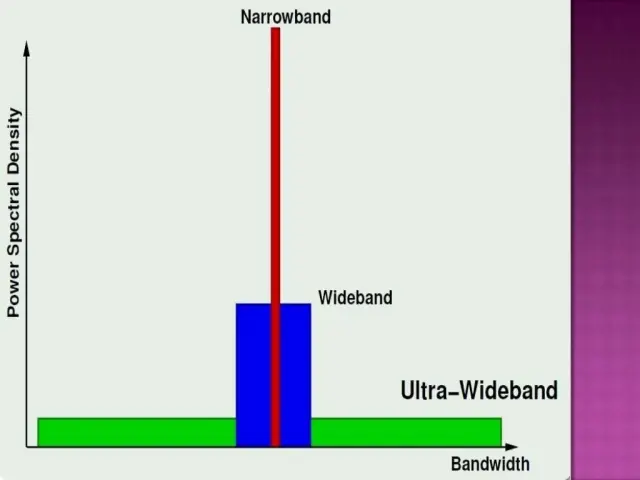
For instance, UWB uses a broad spectrum of frequencies (much higher than WiFi and Bluetooth; in GHz) which translates to significantly higher bandwidth (faster transfer speed). In addition, it consumes much less power than WiFi and Bluetooth standards. However, there is a downside to it. Due to the higher frequency, it can’t travel farther or penetrate obstacles like walls — similar to the 5GHz WiFi band or 5G mobile network.
例如,UWB使用广泛的频率(远高于WiFi和蓝牙;以GHz为单位),这意味着更高的带宽(更快的传输速度)。此外,它比 WiFi 和蓝牙标准消耗的电量要少得多。但是,它有一个缺点。由于频率较高,它不能传播得更远或穿透墙壁等障碍物——类似于 5GHz WiFi 频段或 5G 移动网络。
There is one important dimension to UWB that you should make note of: positional accuracy. UWB can find the direction and precise location down to the centimeter level of a device. Due to such high accuracy, UWB is considered as the best wireless protocol for locating and communicating with devices in a quick and accurate manner.
UWB有一个重要维度值得注意:定位精度。UWB可以找到设备厘米级的方向和精确位置。由于如此高的精度,UWB被认为是以快速准确的方式定位设备并与之通信的最佳无线协议。
Thus, UWB constitutes as a short-range Personal Area Network (PAN) that features high frequencies, high transfer speed, low-power consumption and precise positional accuracy. A perfect standard for quickly discovering and sharing huge chunks of data between devices.
因此,UWB是一种短距离个人局域网(PAN),具有高频率、高传输速度、低功耗和精确定位精度等特点。在设备之间快速发现和共享大量数据的完美标准。
UWB operates in very high frequencies, to be precise, within the range of 3.1 to 10.6 GHz. In other words, this is simply another category of radio spectrum. Coming to the working mechanism, a UWB-equipped device emits signals (called pulse radio) over a large bandwidth in all directions. By the way, since the frequencies are so high, it does not interfere with other nearby radio signals which is a big advantage.
UWB在非常高的频率下运行,准确地说,在3.1到10.6 GHz的范围内。换句话说,这只是无线电频谱的另一类应用。关于其工作机制,配备UWB的设备在各个方向的更大带宽上发射信号(称为脉冲无线电)。由于频率如此之高,因此它不会干扰附近的其他无线电信号,这成为其很大优势之一。
When another UWB-equipped device picks the pulse radio, it relays the information to the host device. Now using Time-of-flight (ToF) and Angle-of-arrival (AoA) data, the device determines the distance and accurate position of the emitting device. If you have read anything about Bluetooth 5.1, you would know that Bluetooth uses the same technique to find the direction of devices.
当另一个配备 UWB 的设备选择脉冲无线电时,它会将信息中继到主机设备。该设备使用飞行时间(ToF)和到达角(AoA)数据,确定发射设备的距离和准确位置。如果您了解有关蓝牙 5.1 的内容,您就会知道蓝牙如何使用相同的技术来定位设备。
However, due to the higher frequencies used in UWB, the host device is able to repeat pulse radio tremendously within a second, making the device instantly discoverable. This immediate broadcasting of pulse radio is called repetition rate and it’s usually within the range of two gigapulses per second (which is an astronomical figure). Due to this high repetition rate, UWB is able to instantly discover, locate and transfer data without losing any moment. And that is how UWB brings immediate spatial and directional awareness around a device.
然而,由于UWB中使用的频率更高,主机设备能够在一秒钟内极大程度地重复脉冲无线电,使设备即刻被发现。这种脉冲无线电的即时广播称为重复率,通常在每秒两千兆脉冲的范围内(这是一个天文数字)。由于这种高重复率,UWB能够立即发现、定位和传输数据,而不会浪费任何时间。就是通过这种方式,UWB为设备带来即时的空间和方向感知。
How is UWB Different From Bluetooth and WiFi? UWB与蓝牙和WiFi有何不同?
The primary difference between UWB and Bluetooth/WiFi is the lack of positional and directional abilities in the latter. While Bluetooth did bring direction finding with 5.1 release, it’s not as fast and accurate as UWB. On top of that, Ultra Wideband consumes much less power than Bluetooth and WiFi because UWB generates radio energy at specific time intervals instead of random frequency response.
UWB 和蓝牙/WiFi 之间的主要区别在于后者缺乏位置和方向判定能力。虽然蓝牙确实在 5.1 版本中带来了测向功能,但它并不像 UWB 那样快速和准确。最重要的是,超宽带(UWB)比蓝牙和 WiFi 消耗的功率要少得多,因为 UWB 在特定的时间间隔而不是随机频率响应中产生无线电能量。
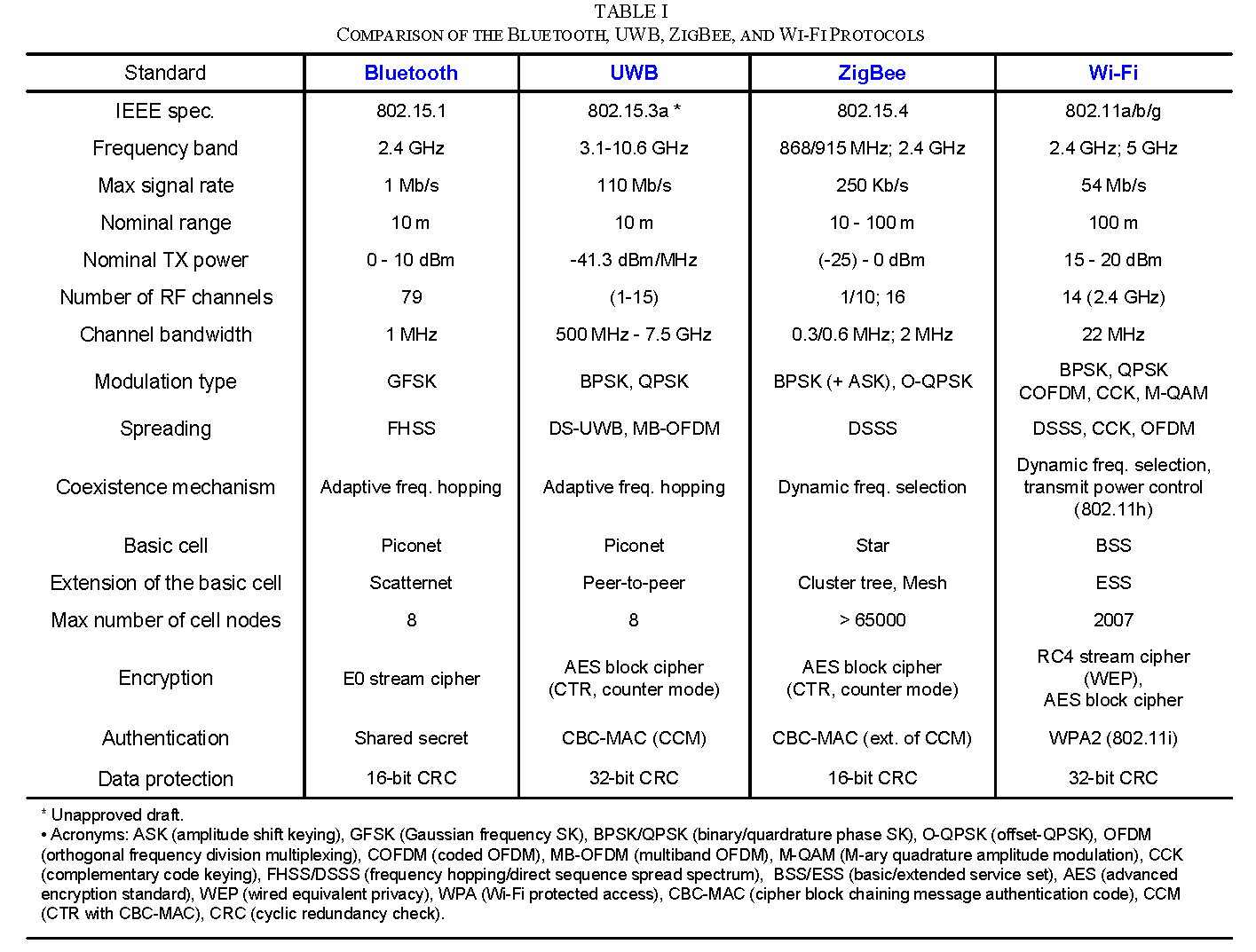
Apart from that, there is a categorical difference in how all three technologies leverage radio frequency. While Bluetooth operates within the frequency band of 2.4GHz (channel bandwidth of 1MHz), WiFi generally operates in 2.4GHz and 5GHz (channel bandwidth of 20 – 40MHz). Lastly, UWB operates from 3.1GHz to 10.6GHz (channel bandwidth ranges from 500MHz to 7.5GHz). By the way, the more the channel bandwidth, the better the transfer speed.
除此之外,在利用射频带宽的方式上,这三种技术存在绝对差异。蓝牙在2.4GHz(信道带宽为 1MHz)的频段内运行,而 WiFi 通常在 2.4GHz 和 5GHz(信道带宽为 20 – 40MHz)运行。最后,UWB的工作频率范围为3.1GHz至10.6GHz(信道带宽范围为500MHz至7.5GHz)。顺便说一句,通道带宽越大,传输速度越好。
Finally, there is a difference in the objectives of all three wireless technologies. For instance, WiFi is used for long-range internet communication from a LAN; Bluetooth is used for short-range, low-bandwidth communication and finally, UWB has its own purpose — short-range, high-bandwidth communication with directional awareness.
最后,这三种无线技术的目标性方面存在差异。例如,WiFi用于从LAN进行远程互联网通信;蓝牙用于短距离、低带宽通信;UWB 拥有自己的独特用途——具有方向感知的短距离、高带宽通信。




